给你一个整数数组 nums 。数组 nums 的 唯一性数组 是一个按元素从小到大排序的数组,包含了 nums 的所有非空子数组中不同元素的个数。
换句话说,这是由所有 0 <= i <= j < nums.length 的 distinct(nums[i..j]) 组成的递增数组。
其中,distinct(nums[i..j]) 表示从下标 i 到下标 j 的子数组中不同元素的数量。
返回 nums 唯一性数组 的 中位数 。
注意,数组的 中位数 定义为有序数组的中间元素。如果有两个中间元素,则取值较小的那个。
说实话题目意思都没看懂
- 输入:nums = [3,4,3,4,5]
- 输出:2
- 解释:
- nums 的唯一性数组为 [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3] 。唯一性数组的中位数为 2,因此答案是 2 。
结合样例是大概看懂了:
题目的意思是说, 给定nums数组, 然后计算唯一性数组的中位数, 而唯一性数组要经过排序
原本对于nums=[3,4,3,4,5], 在排序之前, 唯一性数组应该是这样的
(现在规定distinct(nums[i..j])表示下标 i 到下标 j 的子数组中不同元素的数量, 例如distinct(nums[0..1]) 就是1, distinct(nums[0..2]) 就是2, distinct(nums[0..3]) 还是2 ,因为nums[0..3]是[3,4,3], 只有两个不同的元素)
[distinct(nums[0..1]), distinct(nums[0..2]), distinct(nums[0..3]), distinct(nums[0..4]), distinct(nums[0..5]), distinct(nums[1..2]) .... distinct(nums[4..5])] 一共10个元素 $\sum^{1}_{5}$
然后要对它进行排序
那我们先按照这个思路来做
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| use std::collections::{hash_map, HashMap};
impl Solution {
pub fn median_of_uniqueness_array(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut distinct = Vec::new();
let mut hash_map:HashMap<&i32, i32> = HashMap::new();
let len = nums.len();
for i in 0..len{
hash_map.clear();
for j in i..len{
if hash_map.contains_key(&nums[j]){
let temp = hash_map.get(&nums[j]);
let a = temp.unwrap() + 1;
hash_map.insert(&nums[j], a);
}else {
hash_map.insert(&nums[j], 1);
}
distinct.push(hash_map.len());
}
}
distinct.sort();
println!("{:?}", distinct);
distinct[(distinct.len() + 1) / 2 - 1] as i32
}
}
|
初步得到的代码, 但是很显然, O(n*n)的时间复杂度, 超时了
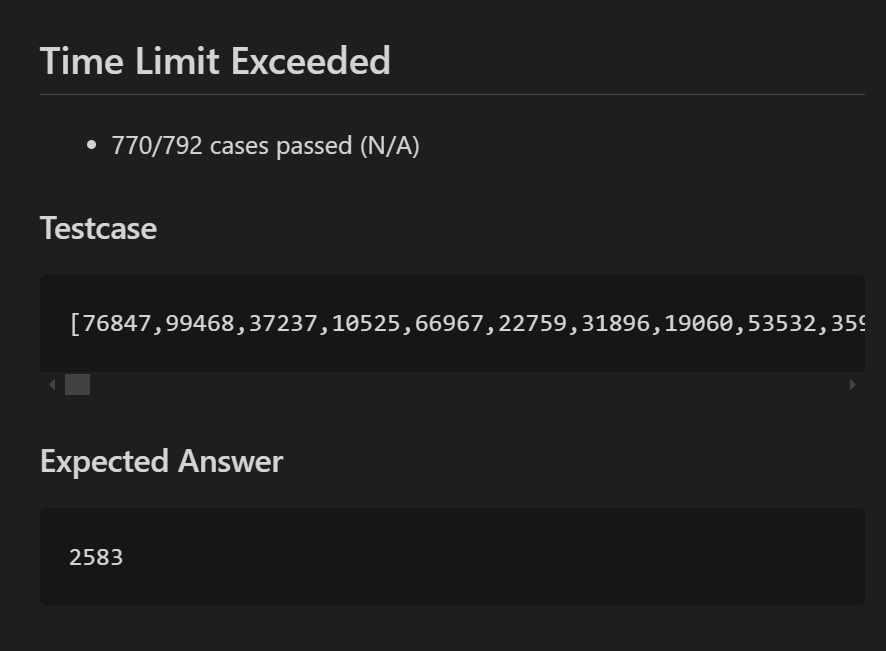
如何优化?
没思路了
直接看题解
二分查找优化, 问题在于如何定义这个二分?
我们直接看官方给出的题解代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| impl Solution {
pub fn median_of_uniqueness_array(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = nums.len() as i64;
let median = ((n * (n + 1) / 2 + 1) / 2) as i64;
let mut res = 0;
let mut lo = 1;
let mut hi = n as i32;
fn check(nums: &[i32], t: usize, median: i64) -> bool {
let mut cnt: HashMap<i32, i32> = HashMap::new();
let mut j = 0;
let mut tot = 0 as i64;
for (i, &v) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
*cnt.entry(v).or_insert(0) += 1;
while cnt.len() > t {
*cnt.entry(nums[j]).or_insert(0) -= 1;
if *cnt.get(&nums[j]).unwrap_or(&0) == 0 {
cnt.remove(&nums[j]);
}
j += 1;
}
tot += (i - j + 1) as i64;
}
tot >= median
}
while lo <= hi {
let mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if check(&nums, mid as usize, median) {
res = mid;
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
lo = mid + 1;
}
}
res
}
}
|
要求中位数 其实就是要求 子数组中不同元素的个数.
假设我们给定一个数median, 就是中位数的位置, 就是说有子数组不同元素的个数要少于n, 这样的子数组的个数要大于 median
总结:
二分还是很要思路的, 还要多练